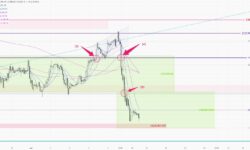
Gold price experienced the largest single-day decline in recent months last Friday, downed by $82. The price stayed within the range of 2320-2360(1) early last week until Wednesday after a disappointing ADP employment figure was released. It cleared the resistance(2) in the Asian session on Thursday. The breakout triggered a new round of buying, resulting in a weekly high of 2387(3) within 24 hours. However, the gold price started selling at the European session on Friday, again back into the previous sideways range(1). After the release of US employment data that evening, the price fell below 2320(5) and touched our target of 2300, closing at the weekly low near 2286.
As mentioned last week, the gold market is in a profit-taking cycle. The latest data from the COMEX gold futures shows that the open interest continues to decline, at 440,000 contracts now. This is about 90,000 contracts less than the peak when gold prices reached a historical high a few weeks back. This indicates that the long buying is still on the limited side, and there is still room for further decline. The key events this week are the US inflation data and the FOMC meeting on Wednesday. Take advantage of a range-bound market while investors are waiting for these economic figures at the beginning of the week. From the M-T perspective, gold prices are still in the phase of consolidation. It will be a good chance to short-sell the market if the high level of uncertainty this week leads to a jump in gold prices.
1-hr chart > The key support level is at the previous low of 2280-2285(6). Expect the price to be bounded within the range of 2280-2320(7), while the market is waiting for Wednesday’s news. A new round of selling will be triggered if the price breaks through the support zone(6).
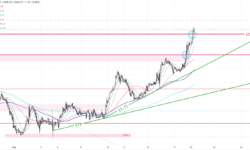
Daily Chart > Gold cleared the ascending channel(9) last week. The closing near the weekly low on Friday indicates that the selling is still dominating the market, and the price might have another attempt to the low in the next 2 days. In S-T, support lies at the previous low of 2277 (10). If there is a successful breakthrough below 2277(10) later this week, the first target can be set at the 50% retracement level around 2216(11).
P. To