Gold Trend 28/10
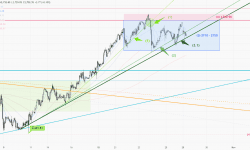
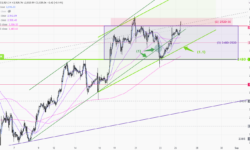
The gold price hit our S-T target of 2750 last week, reaching a new high of 2758. However, the upward momentum failed to last, and the price couldn’t hold above 2750, dropping back to the weekly low of 2708. Towards the end of the week, the gold market once again priced in the risk premium ahead of the weekend’s geopolitical uncertainties, pushing the price back to 2750, and closing the week at 2747.
Last week, several Federal Reserve officials made comments suggesting a ‘cautious approach to rate cuts,’ which strengthened the US dollar and put pressure on gold prices. On the other hand, the market had been grappling with potential retaliatory actions from Israel against Iran for the past two weeks, which finally materialized over the weekend. The attacks were relatively restrained, focusing solely on military sites in Iran and avoiding oil and nuclear facilities. Tehran, so far, has not issued an immediate response. With no significant casualties, the geopolitical tensions eased as markets opened on Monday. The NYMEX oil, most directly affected, gapped open 4% lower, and gold prices also opened $10 lower.
A few crucial US data releases are scheduled from Tuesday to Friday this week, including consumer confidence, third-quarter GDP, core PCE inflation, non-farm payrolls, and the unemployment rate. A lot of uncertainty fills the week, but… considering most of the US economic figures released in the past few weeks have been relatively strong, we can anticipate downward pressures on gold prices prior to the outcome of these figures. As the US election enters its final stages, regardless of the outcome, there is a strong likelihood that the gap between the two candidates will narrow before election day, potentially leading to safe-haven funds flowing into the gold market to support the price, offsetting the downward pressure from strong data.
>
1-hr chart (above) > The price failed to hold above 2750 last week, causing the S-T trend to break below the upward support line (1). The upward momentum has begun to slow down, the support has shifted from the mid-week support line(2) to a slower pace(2.1) before the weekend. The key resistance zone is now sitting at last week’s high of 2750-2758 (4). If any US data falls short this week, the gold price may break above this resistance, triggering a new round of buying. However, before all those economic figures from the US, we can take advantage of the sideway range of 2710-50 (3) for S-T trading.
>
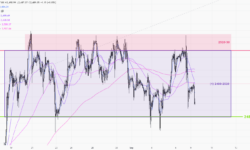
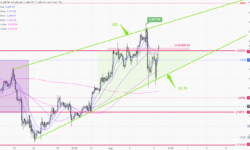
日線圖 (上圖) > 整體格局未有太大改變,關鍵阻力在 2750(5),而上升通道(6)仍然有效。
P. To